44 risk of zero coupon bonds
What Are Zero Coupon Bonds And Their Risks- Tavaga | Tavagapedia Zero-Coupon Bonds can render great returns if used strategically for your investment goal. In absence of any exceptional case, like intermittent coupon payments, Zero- Coupon Bond's yield to maturity is calculated as: Yield = (FV/PV) 1/n - 1 Where, FV = Face value PV = Present Value n = number of periods Example Risk-Neutral Pricing Formula for Zero-coupon bonds with Default Risk 1 Answer Sorted by: 1 A brief educational note and then where you can find the info... As a first step, set the expected payoff equal to 0 where prob_D = probability of default, cur_Px = current price, mat_Px = maturity payment, and R = recovery. Therefore prob_D * (recovery - cur_Px) + (1 - prob_D) * (mat_Px - cur_Px) = 0 results in
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Unique Risks of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds Because of their sensitivity to interest rates, zero-coupon Treasury bonds have incredibly high interest rate risk. Treasury zeros fall significantly...

Risk of zero coupon bonds
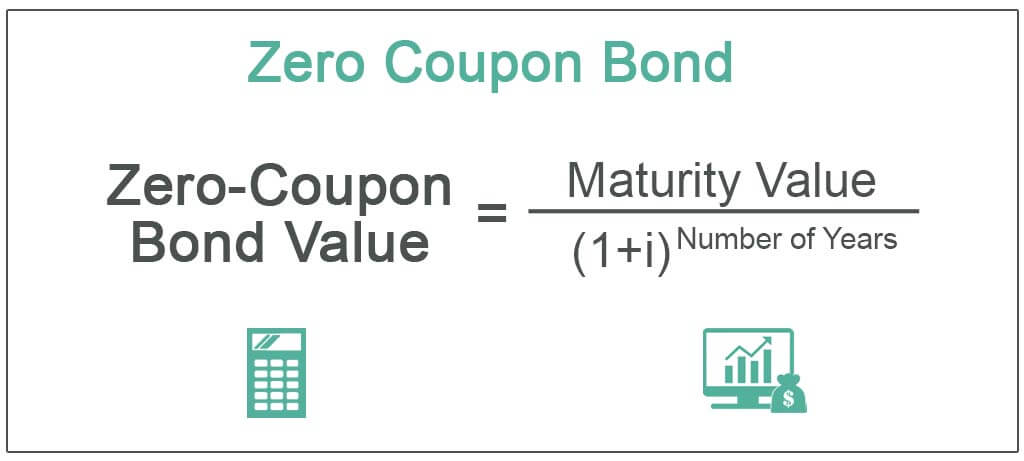
Zero Coupon Bond Value - Formula (with Calculator) - finance formulas A 5 year zero coupon bond is issued with a face value of $100 and a rate of 6%. Looking at the formula, $100 would be F, 6% would be r, and t would be 5 years. After solving the equation, the original price or value would be $74.73. After 5 years, the bond could then be redeemed for the $100 face value. Zero-Coupon Bond - The Investors Book Definition: A zero-coupon bond, as the name suggests, it is a financial instrument which does not allow a regular interest payment to the investor. Moreover, it is a bond which is issued at a meagre market price (discounted price) in comparison to its face value. And it is redeemable on or after a specified maturity date at the par value itself. Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds Unique Risks of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds Because of their sensitivity to interest rates, zero-coupon Treasury bonds have incredibly high interest rate risk. Treasury zeros can easily fall 30% or more in a single year if the Fed raises interest rates. They also have no interest payments to cushion a fall.
Risk of zero coupon bonds. Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Because zero coupon bonds pay no interest until maturity, their prices fluctuate more than other types of bonds in the secondary market. In addition, although no payments are made on zero coupon bonds until they mature, investors may still have to pay federal, state, and local income tax on the imputed or "phantom" interest that accrues each year. How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks Zero coupon bonds are issued by the Treasury Department, corporations and municipalities. The bonds are considered a low-risk investment compared to stocks, commodities and derivatives. Step 1 Mapping Zero-coupon Bonds to Risk Factors - Finance Train This bond has 10 cash flows that are sensitive to different parts of the term structure. The first coupon is sensitive to the 6-month interest rate, the next coupon is sensitive to the one-year interest rate, and the last (10th) payment will be sensitive to the 5-year zero-coupon interest rate. Zero-Coupon Bonds: Pros and Cons - Management Study Guide Higher Yields: Firstly, zero-coupon bonds are perceived as higher-risk bonds. This is because investors pay money upfront and then do not have much control over it. Also, since the money is locked in over longer periods of time, the perceived risk is more.
How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816) The Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds - m.finweb.com Another problem with zero coupon bonds is that they have a higher default risk than traditional bonds. The reason behind this is that companies do not have to make regular interest payments to the investors. They just keep all of the money and do with it as they please. How to Invest in Zero-Coupon Bonds - US News & World Report Zeros are purchased through a broker with access to the bond markets, or with an actively managed mutual fund or and index-style product like an exchange-traded fund. PIMCO 25+ Year Zero Coupon US ... Zero Coupon Bond (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Zero-Coupon Bond vs. Regular Coupon Bearing Bond Advantages #1 - Predictability of Returns #2 - Removes Reinvestment Risk #3 - Longer Time frame Disadvantages #1- Illiquid Secondary Markets #2 - High Duration and Interest Rate Risk #3 -No Regular Income Recommended Articles Explanation
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia Zero-coupon bonds are like other bonds, in that they do carry various types of risk, because they are subject to interest rate risk if investors sell them before maturity. How Does a Zero-Coupon... Zero Coupon Bonds - Contetra Zero-coupon bond (also known as discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond issued at a price lower than its face value, with the face value repaid at the time of maturity. It does not make periodic interest payments, or have a "coupon rate," hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par ... Investor's Guide to Zero-Coupon Municipal Bonds Zero-coupon bonds are sold at a substantial discount from the face value. For example, a bond with a face value of $20,000, maturing in 20 years with a 5.5% coupon, may be purchased at issuance for roughly $6,757. At the end of the 20-year investment, the investor will receive the full $20,000 face value. What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks That's true of bonds in general, but zeros are especially sensitive: Since they do not make interest payments, the size of the payoff that you get from the bond depends entirely on its present...
Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool For instance, a 10-year Treasury bond might have a coupon rate of 3%, meaning that each $1,000 face-value bond will make interest payments totaling $30. For Treasuries, that would come in two...
Zero Coupon Bond Definition and Example | Investing Answers A zero coupon bond is a bond that makes no periodic interest payments and therefore is sold at a deep discount from its face value. The buyer of the bond receives a return by the gradual appreciation of the security, which is redeemed at face value on a specified maturity date. Investors can purchase zero coupon bonds from places such as the ...
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... - CFAJournal They are safe investment instruments, and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are said to be the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, in case of longer time duration (a higher 'N'), it might prove to be profitable for the bond holder. Disadvantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Like virtually all bonds, zero-coupon bonds are subject to interest-rate risk if you sell before maturity. If interest rates rise, the value of your zero-coupon bond on the secondary market will likely fall. Long-term zeros can be particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates, exposing them to what is known as duration risk.
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator [Excel Template] Zero-Coupon Bond Risks Interest Rate Sensitivity One drawback to zero-coupon bonds is their pricing sensitivity based on the prevailing market interest rate conditions. Bond prices and interest rates have an "inverse" relationship with one another: Declining Interest Rates Higher Bond Prices Rising Interest Rates Lower Bond Prices
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Risk of Default Corporate zero coupon bonds carry the most risk of default and pay the highest yields. Many of these have call provisions. How big of a discount will you pay? Here is an example of how zero coupon bond prices can change: For example, assume that three STRIPS are quoted in the market at a yield of 6.50%.
Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds | Kiplinger With retirement years away for you and today's low interest rates, we'd advise against buying zeros. These bonds don't make regular interest payments. Instead, they're sold at a big discount to ...
Zero-Coupon Bonds : What is Zero Coupon Bond? - Groww No reinvestment risk: Other coupon bonds don't allow investors to a bond's cash flow at the same rate as the investment's required rate of returns. But the Zero Coupon bonds remove the reinvestment risk. Zero Coupon bonds do not allow any periodic coupon payments and thus a fixed interest on Zero Coupon bonds is assured.



Post a Comment for "44 risk of zero coupon bonds"